使用angr构建二进制程序的cfg
使用angr构建二进制程序的cfg图。
主要目标是分析afl是如何进行基本块的划分的,然后发现angr的静态分析流程图会更细一些,IDA适中,AFL更粗一些。
对所有基本快来说,入度可以很多,但出度最多为2。
对于较大的程序,angr的Accuracy的full生成方案需要相当的内存。
生成可视化的CFG图
使用CFGFast
CFGFast是一种静态缝隙生成控制流图的方案,会比较的Fast。
def cfgfastpng(filename)
proj = angr.Project(filename,load_options={"auto_load_libs":False})
print("----------static-----------")
cfg = proj.analyses.CFGFast()
plot_cfg(cfg, filename, asminst=True, remove_imports=True, remove_path_terminator=True)# 该函数默认产出格式为png
CFGFast生成的cfg图中,在每一处库函数的调用的时候都会产生一个新的块,感觉在后续处理的时候,需要去掉。
使用CFGAccurate
CFGAccurate和CFGFast也是一样的细度,这就是angr的模块分类方式吧,但CFGAccurate出来的流程图要大好多,原因是其很多重复的块,因为CFGAccurate中保存了块之间的上下文调用关系,用于上下文切片会产生号的效果吧,且CFGAccurate没有添加__libc_csu_init这样的地址。
fast和acc的区别在于, 对于fast,如果两个不同的地方都调用了printf,那么在fast中,就会产生两个由printf出去的路径,结果就是本来两个互相之间不能达的地方就变得能够到达了。
直接给出官方的实例的修改版,我使用的angr版本里建议使用main_object替换main_bin,并使用relative_addr, linked_addr, or rebased_addr替换了之前的addr
#! /usr/bin/env python
import angr
from angrutils import plot_cfg
def analyze(b, addr, name=None):
start_state = b.factory.blank_state(addr=addr)
start_state.stack_push(0x0)
cfg = b.analyses.CFGAccurate(fail_fast=True, starts=[addr], initial_state=start_state, context_sensitivity_level=2, keep_state=True, call_depth=100, normalize=True)
for addr,func in proj.kb.functions.iteritems():
if func.name in ['main','verify']:
plot_cfg(cfg, "%s_%s_cfg" % (name, func.name), asminst=True, vexinst=False, func_addr={addr:True}, debug_info=False, remove_imports=True, remove_path_terminator=True)
plot_cfg(cfg, "%s_cfg" % (name), asminst=True, vexinst=False, debug_info=False, remove_imports=True, remove_path_terminator=True)
plot_cfg(cfg, "%s_cfg_full" % (name), asminst=True, vexinst=True, debug_info=True, remove_imports=False, remove_path_terminator=False)
if __name__ == "__main__":
proj = angr.Project("test1", load_options={'auto_load_libs':False})
main = proj.loader.main_object.get_symbol("main")
analyze(proj, main.rebased_addr, "test1")
该示例显示生成了三种图,一种是只有main函数的图test1_main_cfg.png,一种是全函数调用的图test1_cfg.png,还有一种是test1_cfg_full.png的图,显示更加详细的信息。
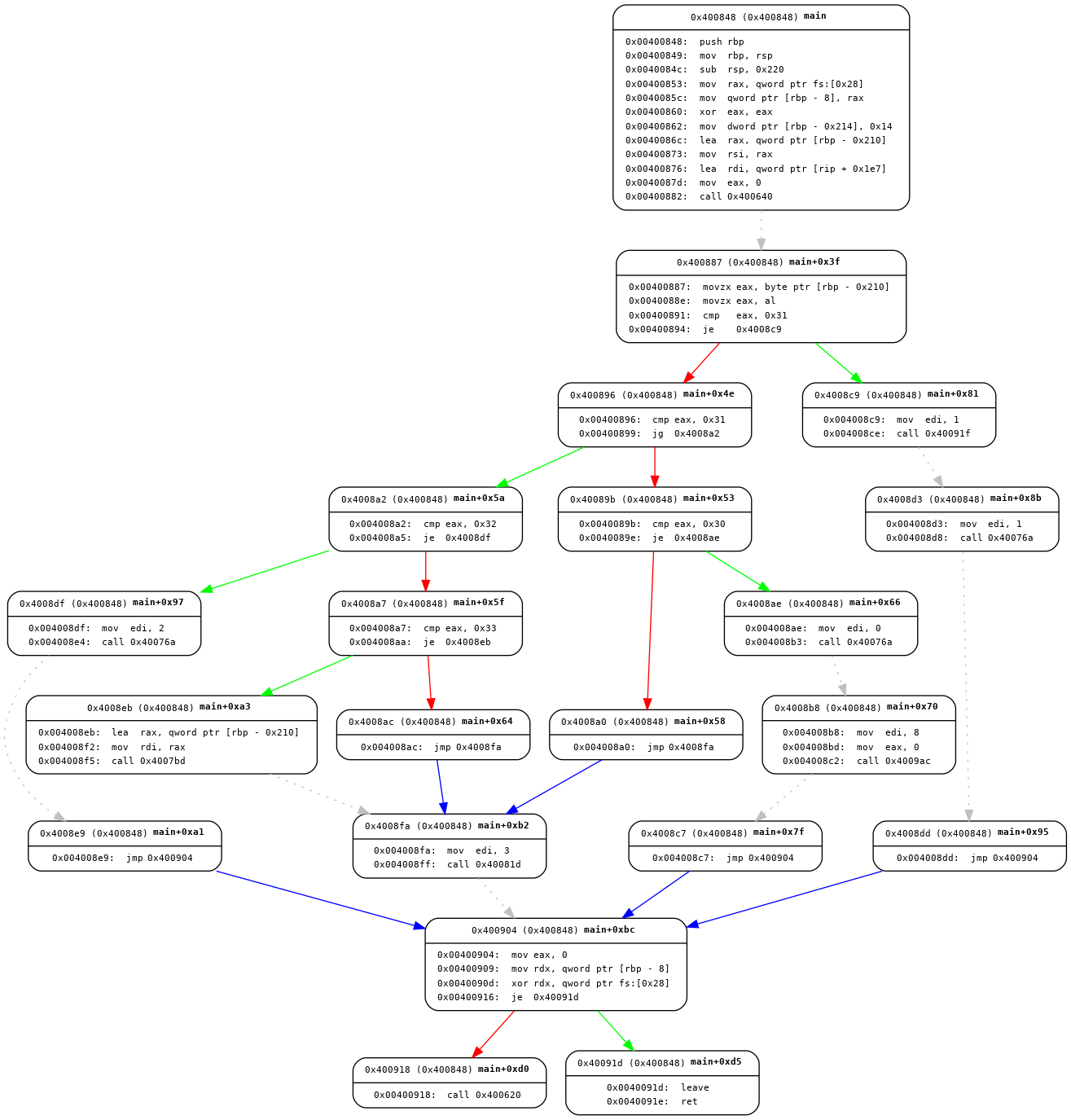
test1_main_cfg.png
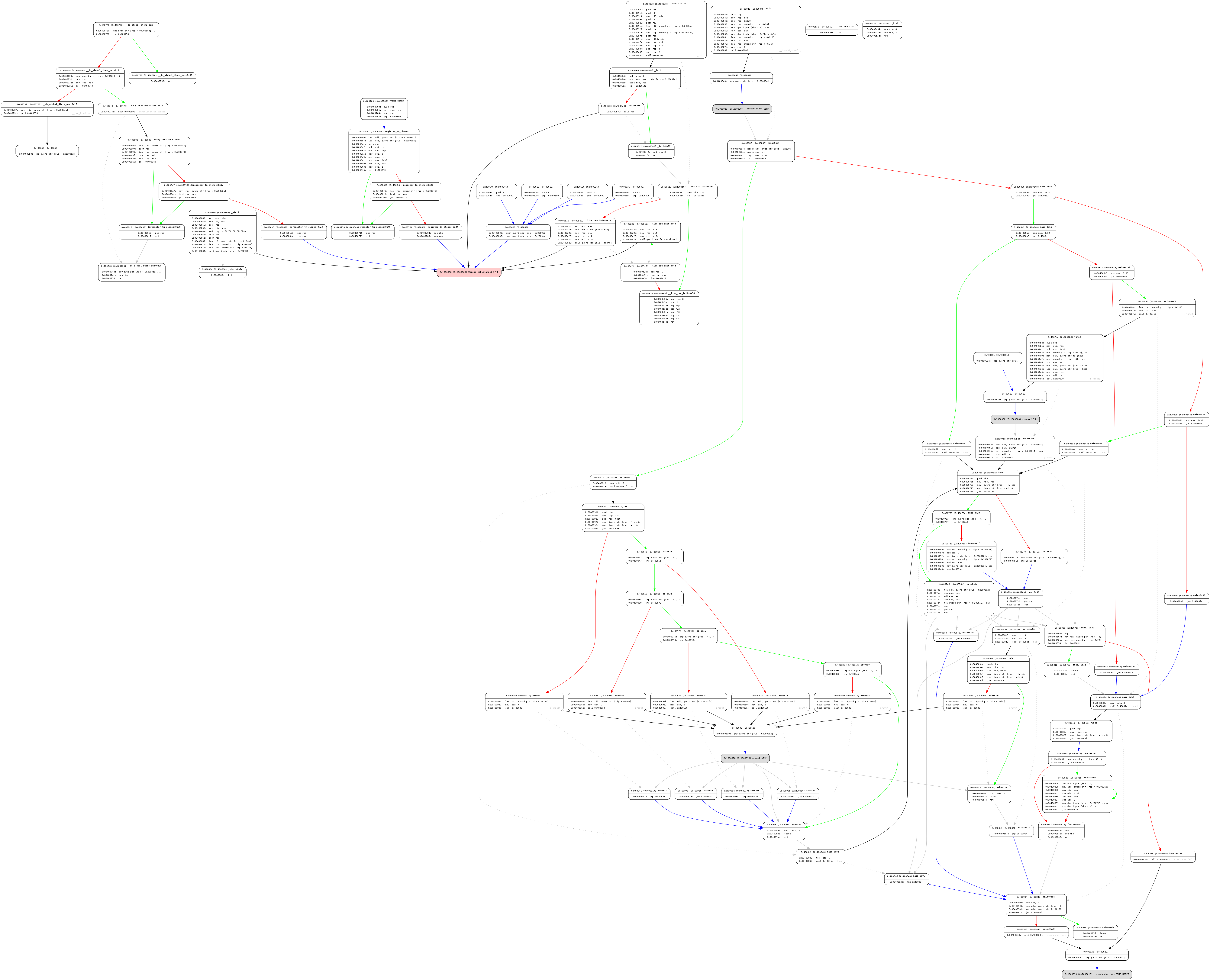
test1_cfg.png
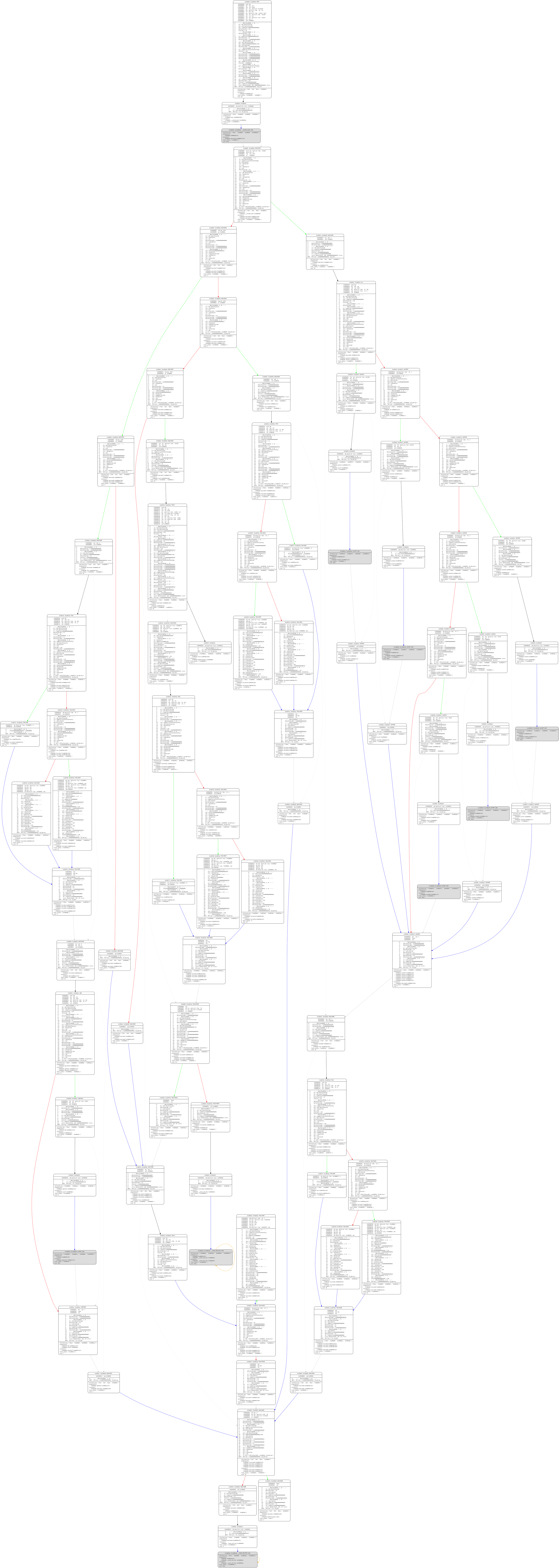
test1_cfg_full.png
可以看到就算是很小的程序,它的cfg图也相当庞大了
生成格式描述的cfg图
angr在这方面封装好了,但从图片中提取信息实在是不容易。。所以找了一下有没有能够获取创建cfg图时用到的dot文件的方法(毕竟安装graphviz和pygraphviz也是废了一番功夫的)。
因此去翻了一下plot_cfg函数的源码
def plot_cfg(cfg, fname, format="png", path=None, asminst=False, vexinst=False, func_addr=None, remove_imports=True, remove_path_terminator=True, debug_info=False):
vis = AngrVisFactory().default_cfg_pipeline(cfg.project, asminst=asminst, vexinst=vexinst)
if remove_imports:
vis.add_transformer(AngrRemoveImports(cfg.project))
if func_addr:
vis.add_transformer(AngrFilterNodes(lambda node: node.obj.function_address in func_addr and func_addr[node.obj.function_address]))
if debug_info:
vis.add_content(AngrCFGDebugInfo())
if path:
vis.add_edge_annotator(AngrPathAnnotator(path))
vis.add_node_annotator(AngrPathAnnotator(path))
vis.set_output(DotOutput(fname, format=format))
vis.process(cfg.graph)
可以看到其参数里是有format的,把format设置为dot就能得到其描述语言版的cfg图了,有每个块的汇编指令。
angr的cfg图特性分析
angr会在每一个call的时候分出两个分支出来,如下面0x400800是main函数的开始地址,第一个块到0x40081d,然后会分成两个块,__afl_maybe_log的块和0x400b22的块,最后__afl_maybe_log的块也会回到0x400822所有没问题。
.text:0000000000400800 lea rsp, [rsp-98h]
.text:0000000000400808 mov qword ptr [rsp+98h+buf+180h], rdx
.text:000000000040080C mov qword ptr [rsp+98h+buf+188h], rcx
.text:0000000000400811 mov qword ptr [rsp+98h+buf+190h], rax
.text:0000000000400816 mov rcx, 140Fh
.text:000000000040081D call __afl_maybe_log
.text:0000000000400822 mov rax, qword ptr [rsp+98h+buf+190h]
.text:0000000000400827 mov rcx, qword ptr [rsp+98h+buf+188h]
.text:000000000040082C mov rdx, qword ptr [rsp+98h+buf+180h]
.text:0000000000400830 lea rsp, [rsp+98h]
.text:0000000000400838 sub rsp, 238h
.text:000000000040083F mov edi, offset unk_402454
.text:0000000000400844 mov rax, fs:28h
.text:000000000040084D mov [rsp+238h+var_10], rax
.text:0000000000400855 xor eax, eax
.text:0000000000400857 lea rsi, [rsp+238h+buf]
.text:000000000040085C call ___isoc99_scanf
.text:0000000000400861 movzx eax, [rsp+238h+buf]